After the popularly known Bitcoin (BTC), which can be referred to be the father of crypto-currencies, comes Ethereum. By market capitalisation, Ethereum is the second largest cryptocurrency with a decentralised open-source blockchain that supports smart contract functionality.
What is Ethereum?
It is important to note that beyond just the crypto idea that spans our knowledge about Bitcoin, Ethereum is more of a software platform that syncs between a decentralised internet and a decentralised app store. Since any entity per se does not control it, a system like this requires some sort of currency to pay for the computational resources required to run these programs. This crypto-currency is known as Ether (ETH).
So, in essence, Ether, in turn, operates as a digital currency and, at the same time, a drive for the decentralised apps within the network. Hence for any change within the network, there is a fee which depends on the gas an action requires, and the amount of required drive determines how much computing power is necessary and how long it will take to run. ‘Ethereum is a public, open-source, Blockchain-based distributed software platform that allows developers to build and deploy decentralised applications’.
The Future of Ethereum
In a centralised system, which is usually controlled by a single entity (the government) and has been valid for hundreds of years, the issue of trust between parties in a transaction has yet maintained its foothold. However, even though history has proved time and time again that it is flawed because it is a single entity control, making apps and online servers utilising this system extremely vulnerable to hacker attacks and even power outages.
Moreover, most social networks and other online servers require users to provide at least some degree of personal information, which is then stored on their servers. From there, it can be easily stolen by the company, its rogue workers or hackers.
On the other hand, the Ethereum system, which is a decentralised one, is completely autonomous as it has been driven by thousands of volunteer computers worldwide, which implies it cannot go offline! Hence users have their information within their grasp while using applications within the network. In this accord, the system has no central point of failure. The system utilises a peer-to-peer approach so that every interaction happens between and is supported only by the users taking part in it, with no controlling authority involved.
What are Nodes?
The entire Ethereum system banks on its anonymity and several volunteers globally download the entire Ethereum Blockchain to their desktops and fully enforce all the consensus rules of the system, keeping the network honest and receiving rewards in return. This set of volunteers around the globe is known as NODES. The Ethereum platform has the potential to profoundly disrupt hundreds of industries that currently depend on centralised control, such as insurance, finance, real estate and so on. Currently, the platform creates decentralised apps for various services and industries.
The road map to Ethereum 2.0
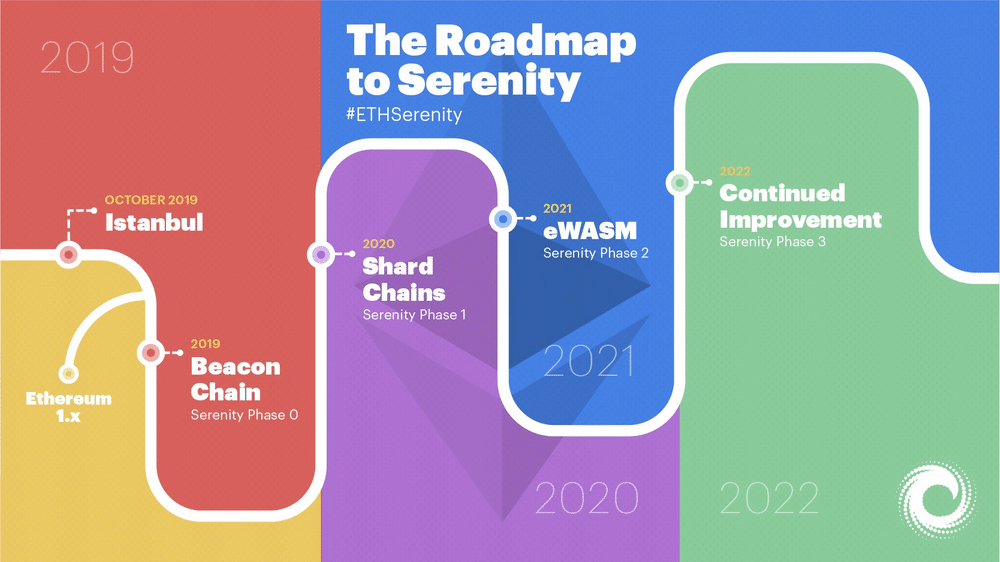
Ethereum took the technology behind Bitcoin and reasonably extended its capabilities. It is a whole network which enables its users to create decentralised applications on Ethereum’s Blockchain. In 2013, the founder of Ethereum, Vitalik Buterin, described his idea in a white paper, which he sent out to a few of his friends, who sent it out further! But unlike Bitcoin, Ethereum is a multipurpose platform.
With its digital currency Ether being just a component of its smart contract applications, and with the capability of bringing its core principles of trust, transparency, security and efficiency into any service, business or industry. Ethereum 2.0 is not completely new for those who have been following the trends of development in the Ethereum community. It is solely a major upgrade to the current Ethereum public main net, designed to fast-track Ethereum usage and adoption by improving its performance.
The overall implication is that for ETH holders, Ethereum 2.0 provides a new opportunity to participate and receive rewards for maintaining the network. Though the upgrade has been split into phases, with the first stage (Phase 0) anticipated to be completed in 2020, this exercise aims to bring scalability and security to the network, such that more transactions can be processed over the network per time with assured security.
DeFi on Ethereum
The Decentralised Finance banks on key principles of the Ethereum blockchain to maximise financial security and transparency, uphold liquidity and growth opportunities, and support an integrated and standardised ecosystem.
The DeFi ecosystem has launched an expansive network of integrated protocols and financial instruments. And with billions of dollars worth of value locked in Ethereum smart contracts, DeFi has emerged as the most active sector in the blockchain space, and its breakthrough is that crypto assets can now be put to use in ways not possible with FIAT or “real-world” assets.
Proof Of Work & the Shard Chain
The existing Proof Of Work architecture has a restriction which has been known since the blockchain foundation. This upgrade will help solve what it suffered from performance issues based on the fact that it relied on a ‘processing-power-intensive’ process known as proof of work to validate and record transactions.
With the introduction of the Proof of Stake and the Sharding upon luncheon of Ethereum 2.0, the proof of stake reforms the crypto-economic incentive structure for validating the blockchain, eradicating the flaws of scalability and accessibility issues to be suffered from the Proof of Work architecture. It works so the node that records each transaction is chosen by an algorithm, with chances of selection stepping up with the amount of the currency the node’s owner holds. This automatically creates a path to decrease the complexity of the cryptographic work, leading to enormous throughput gains for the whole network.
By synchronising Sharding into the whole process, it is expected that the efficiency of Ethereum 2.0 by resource usage will topple (i.e. by breaking data verification tasks up among sets of nodes, and each will be responsible for verifying just the data it has received) other than the initial crude process of verifying each data added to the chain by all the individual participating nodes. What do you think about Ethereum 2.0? Tell us in the comments below!










